

In infrastructure sectors such as transportation and water conservancy, traditional concrete culverts were once the standard choice. However, issues like lengthy construction cycles and poor deformation resistance have gradually come to light. Now, corrugated steel culverts are increasingly becoming the preferred solution in engineering projects due to their unique advantages, offering new approaches to reduce project burdens and enhance efficiency.
Corrugated pipe is a circular pipe formed by rolling corrugated metal sheets or assembling semi-circular corrugated steel plates. Its core feature lies in the corrugated structural design, which reduces self-weight while enhancing the pipe's ring stiffness and load-bearing capacity.
1. Comparative Advantages
As a novel flexible culvert structure, corrugated pipe culverts demonstrate multiple outstanding advantages over traditional reinforced concrete culverts:
(1) Exceptional Structural Adaptability and Cost-Effectiveness
Corrugated pipe culverts exhibit remarkable adaptability to foundation deformation, with low requirements for foundation bearing capacity and levelness. This characteristic makes them particularly effective in adverse foundation conditions such as soft soil, expansive soil, and frozen ground. Their actual construction costs are comparable to or lower than traditional bridges and culverts of similar span lengths. For high-fill sections, the cost per linear meter is approximately ¥3,000 lower than concrete culverts, with post-construction maintenance costs reduced by 70%. Weighing only one-tenth of concrete pipes, transportation and hoisting costs are significantly reduced by 35%. Due to their ease of construction and short project cycles, their lifecycle cost efficiency is even more pronounced.
(2) Streamlined Construction and Significant Schedule Advantages
Compared to traditional concrete culverts requiring months of construction, steel corrugated culvert pipes are factory-prefabricated and assembled on-site, directly reducing project timelines by over 50%. Requiring no heavy machinery, construction is flexible with simultaneous civil engineering and installation, saving substantial labor and time. In a railway project, a culvert originally scheduled for three months was completed in just two weeks, achieving a daily progress rate of 200 meters, enabling rapid traffic resumption with zero disruption.
(3) Superior Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Through specialized surface treatments like hot-dip galvanizing, corrugated culverts form a dense protective layer that effectively resists steel corrosion and oxidation. This ensures long-term safety and durability, with a design service life exceeding 50 years. Adding asphalt coatings or fine-grained concrete linings can extend service life beyond 100 years in corrosive environments, reducing the need for repeated construction investments.
(4) Environmental Protection and Sustainability: A Benchmark Model for Green Construction
By reducing consumption of traditional building materials and construction waste, it aligns with China's dual carbon goals. Its flexible structure and backfill design minimize settlement behind the embankment, enhancing driving comfort and safety. Additionally, materials are recyclable with a recovery rate exceeding 95%. Through integrated technological innovation in projects like Xiong'an New Area's underground utility tunnels, it achieves a seamless fusion of environmental value and engineering functionality.
2. Classification of Different Corrugated Culvert Types, Their Design Principles, and Distinct Applications
Corrugated culverts are not a single product but an evolved family of products tailored to engineering requirements. They can generally be categorized based on factors such as material composition, assembly methods, structural shape, connection types. Each design corresponds to unique mechanical principles and specific application scenarios.
(1) By Culvert Material
Corrugated culverts are primarily classified into two basic types based on material composition:

① Metal Corrugated Pipes:
Steel corrugated pipes, renowned for their high strength, excellent flexibility, and corrosion resistance, are widely used in:
- Culverts, tunnels, and drainage wells for highways, railways, and waterways;
- Temporary bridges and load-bearing structures for bridges;
- Urban sewer pipes, storm drains, and wastewater pipes;
- Underground utility conduits and shared utility trenches; and metal corrugated pipes for small bridge and culvert retrofitting and reinforcement.
② Plastic Culvert Pipes:
Plastic pipes are manufactured by extruding plastic resin mixed with additives like stabilizers and lubricants through a pipe-making machine. Based on material composition, plastic pipes include types such as rigid polyvinyl chloride (UPVC), polyethylene (PE), and polypropylene (PP). Plastic pipes feature light weight, corrosion resistance, and ease of processing. Their material properties determine suitability for diverse environments. Primary applications include: - Water supply piping in building construction - Drainage, venting, and sanitary sewer systems - Underground drainage networks - Stormwater conduits - Conduit systems for electrical installations Each plastic pipe type plays a vital role in its specific application based on performance characteristics.
(2) By Assembly Method
The assembly method directly impacts construction flexibility and the upper limit of structural dimensions.
Corrugated culverts are primarily categorized into the following two basic types based on their assembly methods:

①Prefabricated Corrugated Pipe Culverts;
Description: Circular pipe sections manufactured entirely in the factory, transported to the site, and directly installed and connected via lifting.
Features and Applications:
Advantages: Controllable quality, extremely fast installation speed, excellent sealing performance.
Disadvantages: Limited by transport dimensions, typically smaller diameters (generally less than 3 meters).
Applications: Suitable for standardized projects with small to medium spans, such as common highway round pipe culverts.
② Assembled Corrugated Pipe Culverts.
Description: Corrugated plates are fabricated into standard-sized sections, transported to the site as “prefabricated components,” and assembled using high-strength bolts to form structures of required shapes and dimensions.
Features and Applications:
Advantages: Completely unrestricted by size limitations, enabling construction of giant structures exceeding 10 meters in span; convenient transportation, particularly suitable for remote areas.
Disadvantages: Significant on-site assembly workload with stringent requirements for construction precision and bolt torque control.
Applications: Suitable for all projects involving ultra-large spans, non-standard shapes, or restricted on-site transportation conditions, such as large-scale passage culverts, bridge replacements, and mining tunnels.
(3) By Structural Shape
Structural shape is the core factor determining the performance and application of corrugated culverts. Different cross-sectional forms are designed to accommodate varying loads and spatial conditions.
Based on structural shape, corrugated culverts are primarily classified into the following four basic types:

① Round Type
Design Principle: The circle is nature's most perfect shape under compression. Under uniform radial pressure, the entire pipe wall primarily bears circumferential stress, distributing loads evenly throughout the structure for optimal mechanical efficiency.
Features and Applications:
This is the most common and standard form.
Suitable for standard drainage scenarios with deep soil cover and high loads, such as circular pipe culverts beneath highway subgrades.
Offers maximum vertical and horizontal load-bearing capacity, with mature production processes and high cost-effectiveness.

② Oval Type
Design Principle: By vertically compressing a circular shape, an arch or oval form with a relatively flat bottom is created. This configuration reduces structural height while increasing horizontal span. Its mechanical principle involves utilizing the arch structure to effectively convert vertical loads into lateral thrust, balanced by lateral earth pressure provided by the surrounding soil.
Features and Applications:
Suitable for scenarios with clearance restrictions, such as sections with shallow cover soil, cuttings, or where passage beneath existing structures (e.g., pipelines, utility lines) is required.
The relatively flat bottom provides additional space for dredging maintenance or passage of small animals.
Excellent hydraulic performance maintains a large flow area even at low head.

③ Arch Type
Design Principle: This represents a more extreme arch structure, typically featuring greater spans and lower heights. Its design is entirely based on the mechanics of arch bridges, converting vertical loads from above into immense axial pressure along the arch axis via the arch ring, ultimately borne by robust arch footings.
Characteristics and Applications:
Primarily used where ultra-long spans are required without clearance restrictions, such as replacing small bridges or serving as passageways for livestock or heavy machinery.
Provides a wide, unobstructed passageway with no internal supports, facilitating vehicle traffic.
Demands high-quality foundation treatment at the abutments to prevent horizontal displacement.

④ Horseshoe Type
Design Principle: This asymmetrical structure is specifically optimized for hydraulic performance. Its design mimics natural river channels: during low flow, water concentrates in the narrow bottom section, maintaining high velocity to scour sediment and prevent siltation; during high flow, the upper wide space provides substantial water-carrying capacity.
Features and Applications:
Primarily used in drainage systems with complex hydrological conditions and high sediment content.
Enables “self-cleaning,” significantly reducing maintenance requirements.
Commonly employed in mountainous drainage, river channel management, and mine tailings drainage projects.

(4)By connection method
Corrugated culvert pipes are primarily categorized into four basic types based on their connection methods:
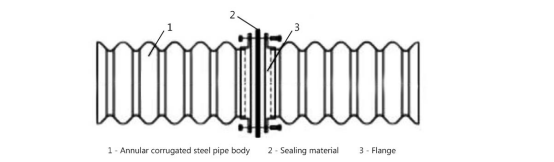
① Internal flange connection: The flange is located inside the pipe, allowing installation without interfering with external backfill soil. This is suitable for space-constrained environments but slightly increases hydraulic resistance.
② External flange connection: The flange is positioned outside the pipe, preserving the inner wall's integrity and smoothness. It offers excellent hydraulic performance and is one of the most common connection methods for prefabricated circular pipes.
③ Lap splicing of plates: Achieved by overlapping corrugated steel plates secured with high-strength bolts. Offers high connection strength and flexibility, making it the preferred method for large-scale assembled structures.
④ Coupling Connection: Utilizes prefabricated corrugated sleeves for rapid installation. Offers simple setup and outstanding sealing performance, particularly suitable for sewage pipelines and projects requiring expedited construction.
Each connection method possesses distinct characteristics. Select the appropriate solution based on specific project requirements.

II. Raw Materials and Manufacturing Process of Corrugated Pipe
The exceptional performance of corrugated pipe stems not only from its ingenious structural design but also relies on high-quality raw materials and precise manufacturing processes. This represents a systematic engineering endeavor integrating metallurgy, mechanical engineering, and corrosion science.
1. Core Raw Materials
Corrugated culvert pipes utilize high-strength low-carbon steel (Q235B, Q345B, or materials compliant with international standards like ASTM A1011) as the base material, ensuring structural strength and formability. Their durability relies on long-lasting anti-corrosion coatings: cost-effective hot-dip galvanizing, superior corrosion-resistant Galfan® (zinc-aluminum alloy), or polymer coatings (PVC/PE) for extreme environments, providing comprehensive protection.
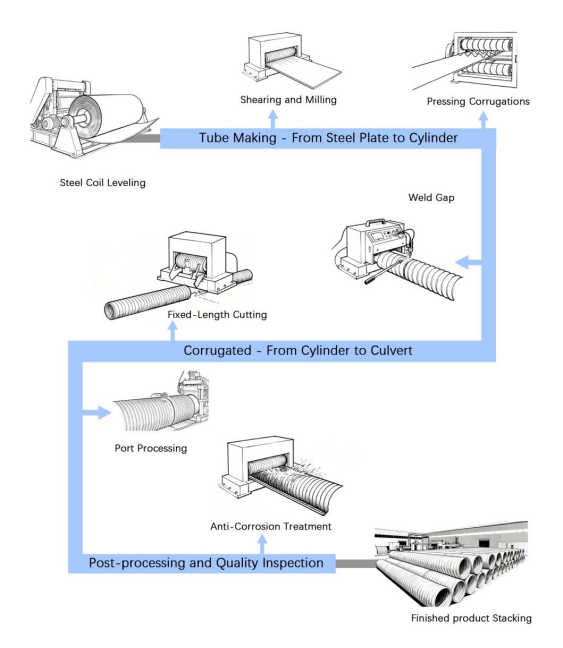
2. Manufacturing Process
The production of corrugated culvert pipes is a highly automated process. Taking the most common “two-step method of pipe forming and corrugation pressing” as an example, the core process flow is detailed below:
Step 1: Tube Fabrication - From Steel Plate to Cylinder
Coil Uncoiling and Leveling: Unroll coiled steel strip material and pass it through multiple sets of rollers to flatten it, eliminating internal stresses and achieving a smooth surface.
Shearing and Edge Milling: Steel plates are cut to design dimensions, with edges milled to create clean, precise weld bevels ensuring subsequent welding quality.
Roll Forming: Flat steel plates are continuously curved into cylindrical shapes using three- or four-roll plate bending machines.
Welding the Seam: Automatic longitudinal welding equipment (e.g., TIG welding) is used to weld the butt edges of the steel plates into a robust, continuous longitudinal weld. This critical process ensures the structural integrity of the pipe body and requires non-destructive testing to guarantee quality.
Weld Finishing and Rounding&Sizing : The weld is ground flush with the base material. The pipe is then passed through rounding rolls to ensure precise cylindrical accuracy.
Step 2: Corrugation Forming - From Cylinder to Culvert
Corrugation Forming: This is the most distinctive and core process. A smooth steel pipe is placed on a large hydraulic forming machine, and a die applies immense pressure from the outside of the pipe wall, pressing regular, continuous annular corrugations onto the pipe wall through a cold-pressing process.
Work Hardening Effect: During the cold-pressing process, the steel undergoes plastic deformation, significantly increasing its yield strength and hardness, further enhancing the rigidity and durability of the corrugated culvert.
Fitting to Length: Continuous long pipes are cut to specified standard lengths according to order requirements.
(If required) Flange Forming: For flanged pipe sections, internal or external flange structures are formed at both ends of the pipe section using specialized rolling or die forming.
Step 3: Post-processing and Quality Inspection
(If required) Assembly Plate Manufacturing: For assembled structures, galvanized steel sheets are stamped into corrugated sheets with overlapping holes in a single press on a large press.
End Face Treatment and Connector Assembly: Burrs on the pipe section ends are cleaned, and matching high-strength bolts, nuts, and sealing washers are installed.
Final Inspection and Packaging: The finished product undergoes rigorous inspection for dimensions, appearance, and anti-corrosion layer thickness. After passing inspection, appropriate packaging (such as stretch film and wooden crates) is used to prevent transportation damage, and labels are affixed, awaiting shipment.
Summary: From the selection of high-quality steel to automated pipe manufacturing, precision corrugated pressing, and long-term anti-corrosion treatment, each process directly determines the final structural strength, durability, and reliability of the corrugated culvert. It is this strict control over raw materials and manufacturing processes that ensures the long-term stable service of the corrugated culvert in harsh underground environments.
III. Product Performance
Having understood the raw materials and manufacturing process of corrugated culverts, we will delve into their superior performance in practical engineering applications.
Structural Performance
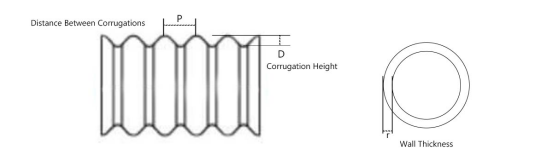
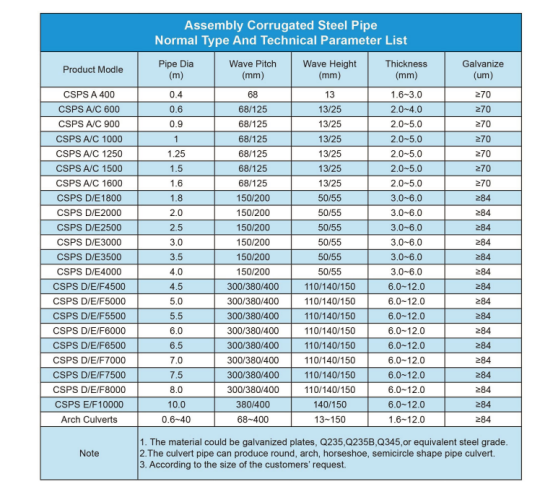
The excellent structural mechanical properties of corrugated culverts stem from their specific wave pitch and wave height design. The unique corrugated structure design effectively enhances the circumferential stiffness of the pipe by increasing the moment of inertia of the cross-section. Whether it is a fully prefabricated or assembled metal corrugated culvert, its structure can work synergistically with the backfill soil to form a composite load-bearing system, converting vertical loads into circumferential stresses. This characteristic gives it excellent resistance to deformation and adaptability to foundations, making it particularly suitable for soft soil foundations, seismically active areas, and engineering conditions with frost heave risk. It fully meets the heavy load requirements of the AASHTO standard and maintains reliable structural stability within the specified overburden depth.
Hydraulic Performance
In terms of drainage efficiency, corrugated culverts exhibit stable hydraulic characteristics. The Manning coefficient of the inner wall of a standard corrugated structure is typically in the range of 0.024-0.030. Although slightly higher than that of smooth-walled pipes, it can meet the drainage requirements of engineering projects through reasonable pipe diameter design and slope selection. For applications requiring higher drainage efficiency, an improved design using polymer lining can optimize the Manning coefficient to 0.012-0.015, while significantly improving the wear resistance of the pipe wall. It is worth emphasizing that the inner wall characteristics of corrugated culverts do not deteriorate over time, effectively avoiding the biofouling and mineral scaling problems common in traditional drainage pipes, ensuring long-lasting and stable drainage capacity. This characteristic is particularly important for long-term use.
Durability and Lifespan
In terms of durability, modern corrugated culverts employ a systematic anti-corrosion protection solution. Standard hot-dip galvanizing provides corresponding protection periods based on the environmental corrosion level, with a design life of over 50 years in conventional engineering environments. For special corrosive environments, enhanced protection systems such as galvanized aluminum coating and galvanized polymer dual coating have been developed, effectively coping with highly corrosive environments such as coastal areas, saline-alkali zones, and industrial zones. These mature anti-corrosion technologies, combined with the product's structural stability, ensure stable performance of the culvert throughout its entire lifespan, significantly reducing maintenance needs and total lifespan costs.
IV. Purchasing Guide and Suggestions
1. Flowchart for Key Parameter Selection:

2. Case Studies of Domestic and International Product Applications
(1) Application in Railway Engineering China - Qinghai-Tibet Railway (High-Altitude Permafrost Zone and Cold Weather Challenge)
In the emergency repair project of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway, the 8-meter diameter corrugated steel culvert, under extreme temperature differences of -40℃ to 25℃, relied on its flexible deformation capacity and cement-free rigid foundation construction method to achieve an overall settlement of only 8 mm, successfully coping with the foundation deformation caused by repeated freeze-thaw cycles in the permafrost region. This made it the standard solution for culvert engineering in the permafrost region of the plateau, and it was widely promoted in subsequent projects such as the Lhasa-Nyingchi Railway.

(2)Application in Highway Engineering: Trans-Canada Highway in Canada (Rapid Replacement of Bridges)
In the reconstruction of a section of the Trans-Canada Highway in Canada, the modular prefabrication and rapid assembly characteristics of corrugated culverts were utilized to shorten the original concrete bridge replacement project, which would have taken several months, to just a few weeks without disrupting traffic. This significantly shortened the construction period while ensuring project quality. It also reduced the impact on public transportation, and its overall cost was far lower than that of traditional bridges.

(3)Applications in Mining and Industry A large mine in Australia (heavy load and rapid deployment)
In a world-class large-scale mine in Western Australia, corrugated culverts were used to withstand the massive load of a 400-ton wide-body mining truck and provide a reliable drainage channel for stormwater runoff. Employing thickened steel plates and a reinforced corrugated design, it combines ultra-high structural strength with rapid construction capabilities, perfectly matching the high-intensity use in the mining area and meeting the needs of rapid mine development.

(4) Applications in Emergency Response and Disaster Relief - Global Disaster Emergency Response (Rapid Post-Disaster Traffic Restoration) The application of corrugated culverts in emergency response and disaster relief is mainly reflected in their unique material and structural characteristics. Faced with traffic disruptions caused by disasters such as floods and earthquakes, corrugated culverts, due to their high strength and axial corrugations, can effectively disperse load stress and quickly build temporary or permanent passages on damaged road sections, buying valuable time for rescue. Therefore, they are listed as strategic materials for reserve by emergency departments in many countries.
V. Industry Development Trends
The corrugated culvert industry is undergoing a profound transformation. According to the latest industry report released by Global Market Insights Inc., the global corrugated steel pipe market is maintaining steady growth, exceeding $5 billion in 2023, and is expected to continue expanding at an average annual rate of approximately 6.5% until 2032. This trend fully demonstrates the increasing importance and acceptance of corrugated culverts in the global infrastructure sector. Its future development shows the following trends:
1.Innovation in Product Materials
The industry is committed to developing next-generation high-performance steels and alloys. Through specific technologies and processes, while ensuring or even improving strength, the weight of the pipe body is further reduced, thereby reducing transportation and installation costs. The latest standard A1060/A1060M-2023 released by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has incorporated high-strength microalloyed steel into the specification, with a yield strength of up to 550 MPa, which is about 40% higher than that of traditional steel. On the other hand, intelligent anti-corrosion coatings are a research hotspot. The CORRDUR project, funded by the EU's Horizon 2020 program, has developed a smart anti-corrosion coating that, according to laboratory verification, can extend the structural design life to more than 100 years.
2. Industry Intelligence and Digitalization
The integration of intelligence and digitalization has become a key direction for industry transformation. The future trend is to pre-embed integrated sensors during pipe manufacturing to monitor the structure's stress, strain, deformation, corrosion rate, and internal water flow in real time. The Japan Society of Civil Engineers' "Technical Guidelines for Smart Infrastructure" lists real-time monitoring systems for corrugated culverts as a recommended solution. Their built-in fiber optic sensors enable continuous monitoring of structural strain and corrosion status, achieving data acquisition. With this data, managers can achieve real-time diagnosis and early warning maintenance of the culvert's health status throughout its entire lifecycle, changing the outdated model of relying on manual inspections and improving the safety and efficiency of infrastructure management.
3. Green Development of the Industry
In line with global "dual carbon" goals, the industry's green development trend is becoming increasingly significant. Data from the World Steel Association shows that using recycled steel to produce corrugated culverts reduces carbon emissions by approximately 58% compared to traditional processes. Corrugated culverts extensively utilize recycled steel as raw material and optimize production processes to reduce energy consumption. Furthermore, due to their inherent recyclability, the circular economy advantages of a "production-use-recycling-remanufacturing" model will be greatly realized. In addition, their compatibility with the concept of sponge cities will be further enhanced. Through optimized design, they can not only drain water but also infiltrate, retain, and purify rainwater, becoming a key component of the blue-green infrastructure network.
4. The Extreme and Diversification of Product Applications
The industry is expanding in two directions: First, it is moving towards extreme application scenarios with larger spans and deeper overburden, continuously breaking through load-bearing limits through structural optimization and material upgrades to replace more small bridges and tunnels. Second, it is developing highly customized and functionally integrated products. For example, multi-functional integrated utility tunnels that integrate drainage, cable laying, and communication pipelines. A 2024 report by the International Tunneling and Underground Space Association (ITA) shows that the annual growth rate of large-diameter corrugated culverts (≥5m) in municipal utility tunnels reached 12%. Related examples include the application of corrugated culverts as dual channels for rainwater infiltration and animal passage, as mentioned above. The EU standard EN 14982:2023 for the first time incorporated ecological corrugated culverts into its regulatory system, requiring them to meet the functional requirements of wildlife passage.
5. Product Standardization and Industry Norms:
With the global proliferation of corrugated culverts, the convergence of design specifications and product standards across countries will become a significant trend. The ISO/CD 19582 standard, currently being developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), will unify global design specifications for corrugated culverts. This standard will integrate key technical indicators from existing standards such as AASHTO (USA), EN (Europe), and JIS (Japan), providing a unified framework for global trade and technological exchange. Simultaneously, based on extensive real-world engineering data, more precise and efficient corrugated culvert design software and selection tools will be widely developed and applied, enabling engineering design to move from experience-based to precise and intelligent. The industry is transforming from a single-product manufacturer to a comprehensive solution provider, further promoting standardization and high-quality development within the industry.
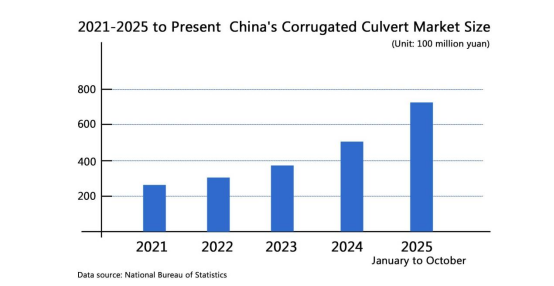
Currently, China's corrugated pipe industry has formed a relatively complete industrial chain and market scale. Statistics show that in recent years, the Chinese corrugated pipe market has continued to grow, with both production and sales showing a steady upward trend. With the increasing investment in infrastructure construction and the deepening of urbanization, the corrugated pipe market is expected to continue its rapid growth in the future. With continuous technological innovation and progress, the performance and quality of corrugated pipe products will be further improved, providing strong support for the industry's development. The corrugated pipe industry will usher in broader development space and opportunities.
Regarding exports, in 2024, the industry as a whole showed a trend of increased volume but decreased price. Export volume increased by 18% year-on-year to 1.42 million tons, but the average export price decreased by 6.3%, reflecting intensified competition in the low-to-mid-end product market. It is worth noting that exports of special corrugated pipes to countries along the "Belt and Road" initiative achieved a breakthrough. Landmark projects such as the Saudi Aramco refinery project and the Indonesian nickel smelting base drove a 34% year-on-year increase in the export value of corrosion-resistant alloy corrugated pipes, reaching US$570 million.
In summary, the corrugated culvert industry is standing at a new starting point. It is no longer merely a "product" replacing traditional solutions, but is evolving into a "comprehensive solution" integrating advanced materials, intelligent sensing, green concepts, and digital tools. Using corrugated steel culverts instead of traditional concrete culverts for culvert construction offers unparalleled advantages in terms of construction time, cost, and environmental benefits. These trends collectively point to a safer, smarter, and more sustainable infrastructure future. CSMC will continue to monitor the future development of corrugated culverts and actively provide useful information to its clients.
We sincerely hope that the information we provide can make more beneficial value. In addition, we sincerely invite you to leave valuable comments and advice on our website. We will follow your comments and advice at any time on our website.
CSMC-Empowering small and medium-scale steel purchasing.
Editor: Hana Kyra
Mail: cs@chinasteelmarket.com




|

|

|

|

|
| Timely Info | Independent | Platform | Multiple guarantees | Self-operated storage |
| About us | Channel | Useful tools |
|---|---|---|
| About China Steel Market | Prices | Steel Weight Calculation |
| Contact Us | Answers | Why Choose Us |
| Terms & Conditions | Inventory | |
| Privacy Policy | Help |
Hot search words: